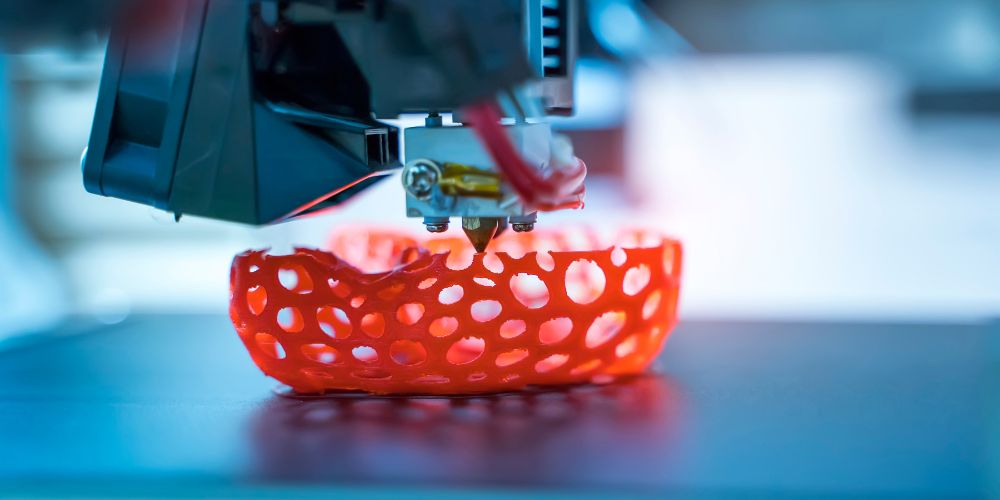
3D Printed Pizza: Is it a Reality?

The impact of technology can be seen in nearly every industry, leaving no stone unturned. The food market is one of the most recent to plunge its toes in the tech field.
3D printers are prevalent recently, building their astounding items a layer at a time from human skin and prosthetic appendage to life-size custom models of the child in your womb, as well as eyeglasses.
It might appear odd that it’s yet intense for a few of us to get our heads around something as normal as 3D printed pizza. With the approach of 3D printing innovation, it was inevitable that an organization saw the chance to foster a remarkable contribution.
All things considered, 3D printed food is a repast arranged through a computerized added substance process. While this definition can be very theoretical (and it is), consider those pizza candy machines that surfaced back in 2015. The batter is ready, expelled, finished off with pureed tomatoes and cheddar, lastly shipped off the stove – all inside a similar machine.
This interaction can be viewed as a crude 3D printing food process. In 2022 we will have elite 3D printing eateries and many food printers accessible. This rapid development in both innovation and public interest has driven numerous to guarantee that, soon enough, every family kitchen will be furnished with its food 3D printer.
In this article, we’ll discuss the whole 3D printed food industry: the cycles, food sources, conceivable outcomes, and current difficulties.
How Does 3D Printing Work?
3D printing is a type of additive manufacturing technology where objects are created by depositing material layer by layer. Unlike traditional manufacturing methods, which involve subtracting material from a larger piece or adding it to build up an object, 3D printing starts with a digital model that is created using a free CAD software or a paid one and then the design is 3D printing by successively adding material until it is complete. This makes it possible to create complex shapes that would be difficult or impossible to create using other methods.
One of the most popular 3D printing technologies is fused deposition modeling (FDM), which melts and extrudes plastic filament to build up an object layer by layer. Other common 3D printing technologies include stereolithography (SLA), selective laser sintering (SLS), and direct metal laser sintering (DMLS).
3D printing has a wide range of applications in many different fields, including medicine, architecture, engineering, and manufacturing.
Which Foods Can be 3D Printed?
A red color 3D printed pizza. Image source: All3DP
First of all, let’s see what kind of food can be 3D printed. If we take a real scenario, 3D-printed food is in its earliest stages and has quite far to go before seeing a more extensive reception from experts and buyers. However, this doesn’t prevent us from wondering about these entrancing machines and their attractive consumable plans.
The food sources that can be 3D printed are restricted to the cycles accessible (as we’ll find in the following segment). Material expulsion is by a wide margin the most well-known interaction for 3D printing food, and, like FDM printing, requires glue-like data sources such as purées, mousses, and other gooey food varieties, for example, chocolate ganache.
Right away, it could feel a piece confined as far as choices; yet, consider every one of the potential blends between mixtures, pounds, cheeses, frostings, and surprisingly crude meats.
How Does it Work?
Pizza loaded with some white cheese. Image source: 3DSourced
Now you will wonder how this machine works. Most of the 3D printing food works similar to printing fiber with a customary FDM 3D printer, as in a gooey material kept onto a surface to make the last item.
While there have been examinations with other added substance processes like fastener streaming and SLS with powdered staples, it’s yet to be proven wrong whether or not these cycles are suitable for food printing. In the meantime, there’s a developing business sector of both expert and prosumer FDM-like food printing machines, as we’ll see later in this article.
The interaction is generally no different for the greater part of these machines: the unrefined substance is taken care of into a needle-like compartment and expelled as the spout is moved around to follow shapes and structure 2D layers each in turn.
Do Food 3D Printers Cook the Food?
Food 3D printers are, for the most part, appropriate for architecting complicated shapes and plans, not for cooking. Usually, the edibles are either prepared for utilization or cooked in an outer stove (or barbecue) when the 3D printing process is done.
There are a few exemptions. The Pancake Bot is a machine that mainly makes hotcakes by expelling the hitter straightforwardly onto a hotplate. It expects somebody to flip it; however, all the other things are finished with similar gear.
Where is it Used?
Today, food 3D printers are generally utilized for connoisseur eating in molecular kitchens or extravagant bread shops. This innovation is not adaptable, requiring additional time and improvement to develop. However, that doesn’t prevent trailblazers and pioneers from utilizing it.
Back in 2016, two famous specialists made another eatery idea in London, named Food Ink. The thought at first was simply to serve 3D printed dishes, yet ultimately, they went similarly as having just 3D printed furniture in the eatery. Food Ink is a voyaging eatery right now on a world visit.
However, not just in top-notch food would you be able to observe 3D printed food. Bread cooks have stood out as truly newsworthy for printing edible wedding cake designs, and for all you pizza sweethearts, 3D printed pizzas have been underway for quite a while and will be a reality as soon as possible.
All the more, plant-based meat is 3D printed to imitate the surface from the genuine article. At the same time, a German organization utilized 3D printers to prepare dinners for seniors who battle to deal with solid food varieties.
So, Where Can I Find it?
Truly, it tends to be challenging to track down 3D-printed food, even in metropolitan regions. Your best bet would be in 3D printing fests or culinary shows, such as 3D food printing meetings, as this innovation has not made much business progress.
Pros & Cons
3D printed food is just regular consumable fixings handled to be expelled through a spout onto a surface. Maybe the fundamental contrast concerning traditional meals is the last show: 3D printing permits mind-boggling, many-sided shapes and calculations that are either difficult to duplicate physically or that would require an unprecedented measure of time.
Benefits
3D printed foods are very safe until and unless prepared with correct procedure in an appropriate machine with proper hygiene and hence can be consumed by us. Moreover, it creates impressive lopping food. Some other benefits of 3D printed food are:
Personalized meals: As far as controlling the variety and measure of supplements, nutrients, and calories per dinner, 3D printed food considers accuracy. This could be critical in medical clinics where limited eating regimens are more regular and offer the potential for simple patient customization.
Unconventional food consumption: At the point when you process nutritious plants and protein-rich bugs in a semi-fluid state, these food varieties could be introduced more appealingly and hence boost their utilization. Later on, even manufactured food may be 3D printed. Who can say for sure!
Easy reproducibility: Sharing plans could be just about as straightforward as moving an advanced record over the web. Everything necessary is similar to unrefined substances, printing settings, and viable printing gear.
Drawbacks
With this large number of intriguing benefits that 3D printed food brings, it comes with a few disadvantages as well. Although time can fluctuate in light of the printer and the printed food, as indicated by Choc Edge, a food 3D printer maker, an exceptionally basic six-layer configuration may require 7 minutes to print. In comparison, more point-by-point 3D models require over 45 minutes each. It probably won’t seem like a lot of a first, yet the entire undertaking needs adaptability at these velocities.
The expense of gear and consumables also presents hindrances as we’ll see straightaway and the time spent preparing. Moreover, the edibles utilized in these machines either require pre-cooking or pre-handling to accomplish the consistency expected for expulsion. Thus, the normal reproducibility and dependability for these machines rely intensely upon the legitimate arrangement of those materials.
Professional Printers
In 2022, there will be just a modest bunch of expert-grade food 3D printers, generally in work area forms, despite everything having no modern size gear. In any case, a portion of the accompanying models is now being utilized for catering, occasions, and eateries. There are also many other professional best 3D printers under $1000 that can be used for 3D printing pizza.
Foodini: This is one of the most advertised food 3D printers of all, and deservedly so. Regular Machines’ Foodini can deal with practically any fixing, from jams to scrumptious burgers, utilizing five unique cartridges simultaneously.
Regular Machines has a sound sustenance approach, giving plans to new clients to get everything rolling before they plan their own. The Foodini is valued at around $4,000.
Conclusion
We’ve covered groundbreaking food technology with its benefits and disadvantages. 3D printed food is going to revolutionalize your kitchen in due time. Stay tuned!